Users are ultimate judges of valuable software.
Whatever the technology or who’s behind the software, failing to meet the users expectations result in a loss of demand.
Confronting ourselves to the reality of our users seems like evidence, but it is a practice too often disregarded by software teams.
Customer Feedback is a Quality Engineering methodology described in this article, aiming at prioritizing valuable software increments by better understanding users.
Follow the QE Unit for more Quality Engineering from the community.
What is Customer Feedback?
Customer Feedback relates to the experiences, perspectives, feelings of your customers using your products and services to solve problems.
The practice of customer feedback is at the heart of customer-centric companies, channeling their effort systematically referring to the customer experience.
Customer feedback develops a better empathy for customers that enables to improve their digital products and services for their needs.
But it’s harder than it sounds.
The Adobe’s 2021 Digital Trends Report shares that only 1 in 5 companies have “significant insight” into their customer’s journeys.
Organizations have to implement feedback through the customer experience, at every touchpoint of interactions to maximize inputs obtained.
Customer feedback has the particularity to focus on existing customers, that is, “users” that did not buy from the company are out of scope.
Feedbacks range from sharing surveys straight after the purchase, a few days after an order has been placed or shipped, or even with more delay until a new order is made.
The main value of Customer feedback is to provide useful information that helps to drive a more valuable software roadmap for Quality at Speed software.
Why use Customer Feedback in Quality Engineering?
Quality Engineering is the paradigm constraining the entire software lifecycle to Quality and Speed for continuous value delivery.
Its implementation relies on progressive practices across MAMOS, where the first domain of Methods is essential to align the actors on building the right thing.
This Harvard Business Review Analytic Services demonstrates that 72% of companies think that they address customer problems, versus 35% from the customers perception.
Customer feedback aims to close that gap.
Closing this empathy gap is what enables organizations to thrive with Quality at Speed software, with improvements in sales growth up to 85% and in margin of more than 25% (Gallop source).
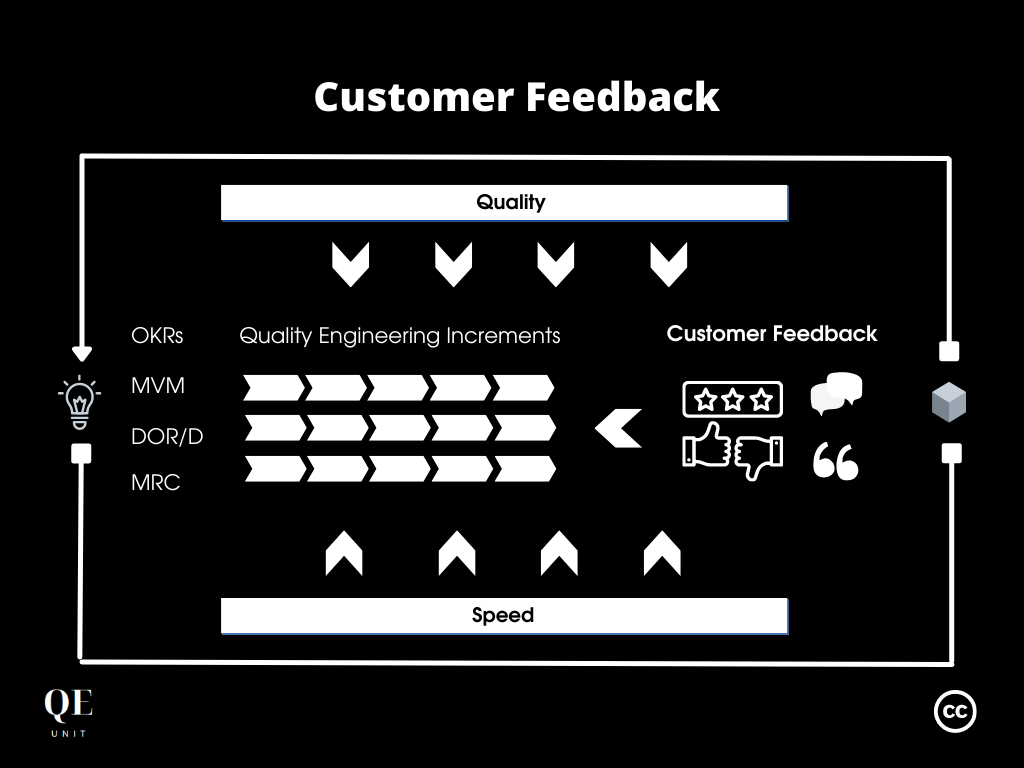
How does Customer Feedback contribute to Quality?
Software teams with a pressure to deliver focus on what to deliver now, continuously iterating over the various features.
This centricity around the software lifecycle makes the team lose sight of the actual use of the software by their customers, not necessarily knowing how satisfied they are.
Applying Customer Feedbacks on a regular basis makes sure to keep the center of attention of the teams on customers, fostering a better empathy and value delivery.
Customer Feedbacks contribute to Quality being:
- Result-driven with concrete feedbacks to implement and results to share
- Systematic applied on a regular basis at various touchpoint of customer journeys
- Scalable by being applicable to many teams and multiple software products.
How does Customer Feedback contribute to Speed?
Speed of delivery in our digital ecosystem requires to continuously deliver valuable software increments to improve the value proposition and generate new revenue streams.
It is necessary to deliver short-term increments that have a high probability of meeting the customer demand to rapidly scale a successful digital offer.
Teams using Customer Feedback improve the likelihood of meeting the customer demand by considering concrete inputs from existing customers that are already using the offers.
Customer Feedbacks contribute to Speed with:
- Focus on the customers, fostering a better empathy and customer-centricity
- Rhythm by being used systematically and to drive roadmap priorities
- Asynchronicity with automation, reports and shareable content
- Visibility by sharing concrete results of feedback mechanisms.
How to start with Customer Feedback in QE?
You have to meet your customers where they are and propose inputs for feedback that are convenient.
The form and options of each feedback will depend on its typology. For example, a NPS score and customer satisfaction (CSAT) will be different.
The three most common types of customer feedback are:
- Product Feedback
- Customer Service Feedback
- Customer Satisfaction Feedback
- Complaints
- Feature Requests
- Sales Feedback.
Then each of this type of feedback can be implemented at different points:
- Customer feedback from support requests
- Customer feedback at call center agents
- Customer feedback inside digital channels
- Customer feedback with a users pool
- Customer feedback via email and sms
- Customer feedback through focus groups
- Customer feedback on social media and community.
Customer feedback from support requests
Support requests are a gold mine of information in regards to the satisfaction, perception and performance of your company offerings.
Many successful startups and large corporations relate stories of having customer support requests routed directly to the CEO and the board to keep in sync with the reality.
Customers demonstrated their interests in your products and services but they can directly limit business growth from a negative experience they will share with their peers.
Make a habit of reading, sharing and analyzing the customer support requests, sharing with your software teams what matters for them, and more broadly in the company.
Customer feedback at call center agents
Call centers are the second important source of customer feedback, where for them, “2% of complaints overall is 100% of their work”.
Some information will cross with other categories, but you will also find new insights and inputs interacting with call centers agents and transcripts.
Ideally, you would have a way to access categorized recordings and transcripts to ease your analysis, but also take the time to interact directly with some agents.
Practicing this exercise on a regular basis yourself directly, and by members of your team will change how people see the contribution of their work.
Customer feedback inside digital channels
Digital channels are your main point of digital interactions with your customers, usually on web, mobile application and other interfaces.
The advantages of digital channels is to ease the access to feedback by injecting forms directly in the digital channel, near the moment you want to capture.
You can implement feedback at each point of customer interactions, for example by leaving a satisfaction form straight after the order has been confirmed.
The advantage of being digital is to ease A/B testing to find the best way to ask for feedback depending on the context and customer profiles.
Customer feedback with a users pool
An alternative to ask your customers on digital channels, is to ask for a pool of users proposed by an external company.
This option is useful when you want to capture specific feedback that is not necessarily suitable to ask your general customers during the buying experience.
Companies specialized in that area help by providing profiles similar to your existing customers, or even one you would like to capture.
That category is a helpful technique still relying on digital channels to ease its implementation, rather than an on-site gathering.
Customer feedback via email and sms
Email and SMS are still largely used by customers for daily interactions, security validation and exchange of information.
The main attention point is to keep things simple to be easily actionable.
Email and SMS asking for feedback of a NPS type must for example directly include buttons to select the answer to provide.
People have less and less patience for reading long emails to understand what is expected. Be direct and straight to the point.
Customer feedback through focus groups
An alternative to digital channels is to interact with customers directly on-site, by implementing focus groups.
This category can generate more insights with a physical presence and more information to capture, from the behavior to the concrete feedback given.
It is quite useful when there is a strong need to visualize the interaction of your customers, for example in the case of a new mobile product or services.
The advantage of such a technique is to combine multiple feedback sources that can capture before, during, and after the experimentation moment.
Customer feedback on social media and community
The last place to gather customer feedback is on online communities, such as social media, forums and user groups.
The good point of such an area is to contain direct feedback between peers, reflecting how customers refer to your product or services, and what is mostly referred to.
The complexity of such feedback is to be very variable in quality, quantity and usually tied to recent interactions, that are most of the time negative ones.
Nevertheless, social media and online feedback must be continuously monitored and answered for your public image, and shared with your team.
Customer Feedback within MAMOS
A continuous link between your customer experience is a must-have to prioritize software changes that will directly improve their journeys.
Some teams think that their best ideas will come from thinking outside of the box, imagining new features. While it is necessary for innovation, the experience must already be good.
Reach the high-standard of Quality Engineering requires to master the fundamental practices with a progressive implementation, where Customer feedback fits in.
Confronting ourselves to the cold reality can be hard, but it is a necessary step for significant improvements and valuable changes, at multiple levels.
Are you already receiving customer requests right in your inbox?
References
Nikolett Lorincz (2022), How to Get Customer Feedback (15 Tried & Tested Methods). Optimonk.
Clint Fontanella (2021), How to Ask for & Actually Get Customer Feedback. Hubspot.
Jen Henderson (2021), How to get customer feedback. UserTesting.
Shelley (2020), 10 Ways to Get Customer Feedback. Aspiration Marketing.